Generally, three-phase electricity (380V), in practical application, only three-phase four-wire system (not counting the ground wire, it is called the three-phase five-wire system if the ground wire is included), and the three-phase three-wire system will not be used. In the three-phase four-wire system, in addition to the three live wires, the fourth wire is called the neutral wire (tips: the single-phase only has the neutral wire, but the three-phase wire does not).
The basic principle of three-phase electricity
If the loads connected to each of the three-phase circuits are the same, and the sum of the currents flowing through the neutral line at each moment is zero, it is possible to remove the neutral line and use a three-phase three-wire system for the power supply. But this is an ideal situation. In fact, the three-phase load formed by multiple single-phase loads connected to a three-phase circuit cannot be completely symmetrical. In this case, the neutral line is particularly important and necessary.
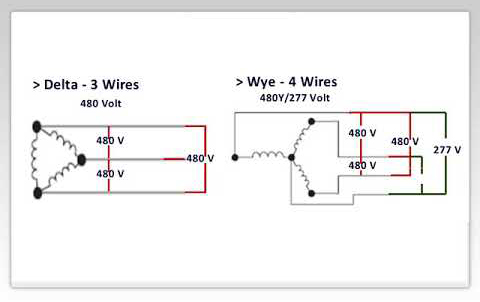
If the load is asymmetric and there is no neutral line, a three-phase three-wire power supply with an asymmetric load is formed. Due to the asymmetry of the load impedance, the phase current is also asymmetric, and the load phase voltage is naturally not symmetrical. Some phase voltages may exceed the rated voltage of the load, and the load may be damaged (the bulb of the phase is too bright and burnt out). Some phase voltages may be lower, and the load cannot work normally (the bulb is dim). The load impedance of each phase changes with the lights on and off. The phase current and phase voltage will change accordingly, the lights will flicker, and other electrical appliances will not work properly, or even be damaged. Therefore, there must be a neutral line, that is, a three-phase four-wire system.
Three-phase voltage stabilizer
- Three-phase three-wire voltage stabilizer: When the three-phase three-wire voltage stabilizer is connected, the output and output lines each have three lines, and these three lines are all three front lines.
- Three-phase four-wire voltage stabilizer: The difference between the three-phase four-wire voltage stabilizer and the three-phase three-wire voltage stabilizer is that the output of the three-phase voltage stabilizer is all four lines, they are made up of three front lines and one neutral line.
Among the three-phase three-wire voltage stabilizers and three-phase four-wire voltage stabilizers, the three-phase four-wire voltage stabilizer is currently the most widely used, and for the three-phase three-wire voltage stabilizer, it will be useful except in very special equipment. In addition to the three-phase three-wire voltage stabilizer, the three-phase three-wire voltage stabilizer is also rarely used and is not commonly used.
